Posts for tag "University of Minnesota"
University of Minnesota’s Cedar Creek Ecosystem Science Reserve: Making Significant Contributions to Ecosystem Studies and Environmental Monitoring since the 1940s
Cedar Creek Ecosystem Science Reserve has a proud history of significant monitoring work that goes back to the beginning of the field of ecosystem ecology. It is also the site of several of the longest field studies...
- Posted July 31, 2019
Scientists Use Wild Rice as Miner’s Canary in Minnesota Waterways
A team has unraveled the mystery of why wild rice won’t grow in water with high levels of sulfate—and the other consequences of sulfate in waterways.
- Posted March 1, 2018
Using Conductivity As A Tracer Yields More Data, Lower Costs
University of Minnesota researchers find that using conductivity as a tracer is more cost-effective and straightforward than other methods.
- Posted November 7, 2016
Lake Malawi Sediment Core Reveals Wet Past
University of Minnesota scientists find that Lake Malawi had a past climate much wetter than previously thought, thanks to sediment analysis.
- Posted August 23, 2016
Instrumenting Castor, Scanlon Lake May Help Sediment Core Analysis
U. of Minnesota researchers study two lakes in Washington state to uncover insights that could improve sediment core interpretation in the future.
- Posted April 11, 2016
New Water Scarcity Map Shows Issues Globally
A team of international researchers has charted water scarcity issues around the world and incorporated their findings into a single map for planners and policymakers, according to a release from the University of Minnesota. The new water...
- Posted January 27, 2016
Increased Plant Growth Likely Not Enough To Counteract Carbon Emissions Increases
Scientists had hoped that more plant growth would mean large additional carbon sink capacity enough to offset carbon dioxide emissions in the atmosphere, but a recent study shows the capacity gained by plants may simply be inadequate...
- Posted December 11, 2015
Scientists Consider Causes Of Increasingly Common Water Contaminants
A study led by the University of Minnesota has found that there is a class of water contaminants present largely due to indirect human actions, according to a release. The contaminants in question are polybrominated diphenyl ethers...
- Posted November 3, 2015
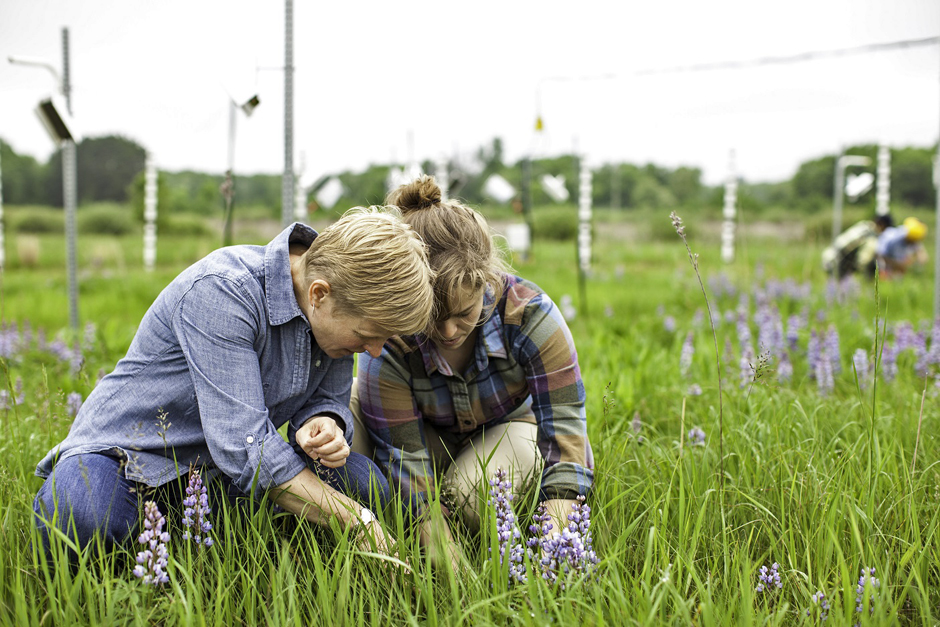
Biodiversity Promotes Grassland Survival During Climate Extremes
Although researchers have long known that biodiversity tends to stabilize plant productivity over time, it wasn’t clear if the stabilizing effect occurred during extreme weather events or after. A study from the University of Minnesota reveals the...
- Posted October 16, 2015
Turning Peatlands Into Oil Palm Plantations Releases More Carbon Than Once Thought
Waterlogged soils known as peatlands are great natural carbon storage systems, but are regularly developed into oil palm plantations. A new study from University of Minnesota suggests that developing peatland into plantations releases twice as much carbon...
- Posted August 4, 2015