Parameters
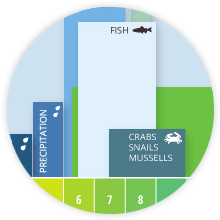
Learn the importance of environmental parameters, typical concentrations, influencing factors and abnormalities.
Measurements
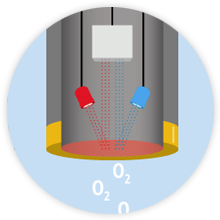
Understand the principles of operation behind various methods used to measure and monitor environmental parameters.
Equipment
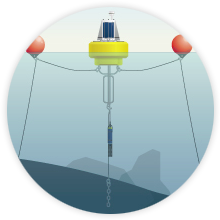
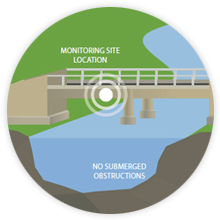
Learn about various sensors, meters and data acquisition systems used in environmental measurements.