Impacts Of Global Temperature Rise Vary By Location
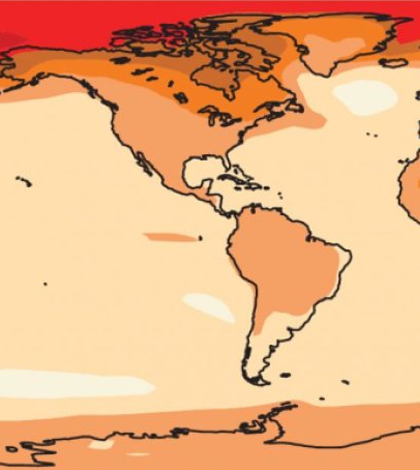
Map showing the increase in regional average temperatures when the global average temperatures reach 2 degress Celsius above pre-industrial levels. (Credit: University of South Wales)
Although a 2-degree Celsius rise in global average temperatures may not sound like a lot, regional variations in the rise may mean significant changes, as much as 6 degrees Celsius higher in some areas inland, according to a release from the University of New South Wales.
In addition, the temperature rise is likely to impact some areas, especially colder ones, more than others. In the Arctic, the projected temperature increase may be as high as 8 degrees Celsius if a global average rise of 2 degrees Celsius occurs. An 8-degree Arctic rise would cause additional ice melt and sea level rise, having global impacts. On the other hand, regions such as Australia are expected to feel little impact even with a 2-degree global rise.
The study is the result of an analysis of global climate change data by Swiss and Australian scientists. Because regional variations were significantly higher than the global average temperature rise in many cases, study authors suggest limiting carbon dioxide emission levels to 600 gigatonnes instead of 850 gigatonnes. The previous limit of 850 was established with a goal of keeping global temperature rise below 2 degrees Celsius.
Top image: Map showing the increase in regional average temperatures when the global average temperatures reach 2 degress Celsius above pre-industrial levels. (Credit: University of South Wales)




0 comments