HOBO Water Temp Pro v2 Logger
The Onset HOBO Water Temp Pro v2 logger is designed with a durable, streamlined, UV-stable case for extended deployments measuring temperature in fresh or salt water.
Features
- Research-grade measurements at an affordable price
- Waterproof up to 120 meters (400 feet)
- Compatible with HOBOware and HOBOware Pro software
- Expedited repair and warranty service
- Lifetime technical support
- More
Overview
Built to withstand extended periods of immersion, the compact HOBO Water Temp Pro v2 Logger provides reliable, accurate underwater temperature measurements. The small size of the logger allows it to be easily mounted and/or hidden in the field.
Durable
The HOBO Water Temp Pro v2 logger is waterproof up to 120 m (400 feet) and rugged enough to withstand years of use, even in stream conditions. It has enough memory to record over 42,000 12-bit temperature measurements.
Mechanics
The Water Temp Pro v2 Logger requires an infrared base station (90706) or shuttle (90707) and HOBOware, available as a free download, or HOBOware Pro software (sold separately) for system launch and data retrieval. The associated couplers are included with both the base station and shuttle. In addition, the shuttle can operate as a base station for added flexibility in the field.
Data Storage
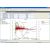
The high-speed infrared communications offloads data in less than 30 seconds (requires USB port), and the infrared communications port is located opposite the bail end for convenient access while tethered. Offload data or check the logger and battery status, even while logging. A blinking LED indicates that the logger is recording data. To reduce visibility in the field, this feature can be turned off. Non-volatile EEPROM memory retains measurements in the event of battery failure.
In The News
Supplying Seattle’s Drinking Water: Using Data Buoys to Monitor the Cedar River Municipal Watershed
Providing clean, safe, and reliable drinking water for the 1.6 million people in the greater Seattle area is a top priority for Seattle Public Utilities (SPU). With limited water supplies, SPU dedicates considerable resources to maintain its watersheds and mountain reservoirs. About 70 percent of Seattle Water comes from the Cedar River Municipal Watershed , and the other 30 percent comes from the South Fork Tolt River Watershed . [caption id="attachment_39574" align="alignnone" width="940"] Data buoy in Chester Morse Lake . (Credit: Kevin Johnson / Seattle Public Utilities) [/caption] Jamie Thompson, a fisheries biologist at SPU, monitors aquatic ecosystems centered on fish listed under the U.S. Endangered Species Act (ESA).
Read MoreData-Driven Advocacy on the Lower Deschutes River
Like many freshwater environments, the Deschutes River in Oregon is under pressure from development, pollution, and climate change. Many rivers, streams and lakes in the Deschutes Basin do not meet Oregon water quality standards –where state water quality monitoring assesses levels of bacteria, pH, dissolved oxygen, temperature, and fine sediment. Hannah Camel is the Water Quality Coordinator for the Deschutes River Alliance (DRA), a non-profit organization that focuses on the health of the lower 100 miles of the Deschutes River–the area most affected by human intervention. As a data-driven organization, the DRA has benefited from the installation of two NexSens X2 data loggers.
Read MoreExpanding the Port Everglades: Real-Time Monitoring of Water Quality Conditions from Planned Dredging Operation
The Port Everglades in Broward County, Florida, serves large trade vessels and cruiseliners and incoming and outgoing recreational boaters. However, as cargo ships become larger, the port must expand. A dredging project led by the US Army Corps of Engineers will substantially deepen and widen the port's navigation channel to accommodate larger Panamax cargo ships and modern cruise liners. As a result of this project, a large amount of sediment will be displaced into the water column. This suspended sediment may settle outside of the project area, burying benthic organisms like corals, and possibly carrying harmful particulates to other regions. [caption id="attachment_39497" align="aligncenter" width="2560"] A CB-950 and CB-25 deployed on site at Port Everglades.
Read More